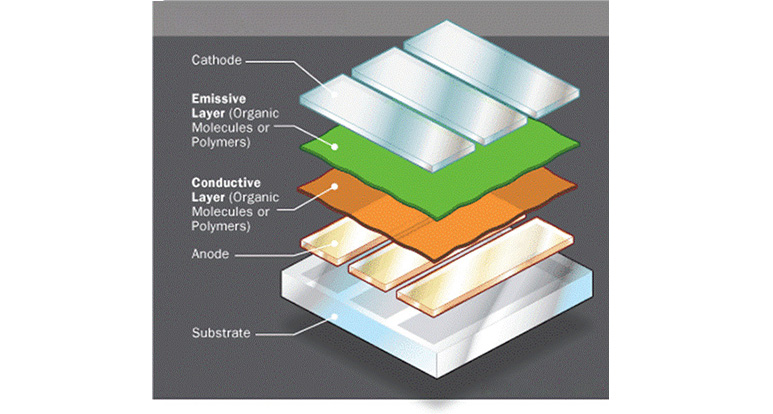
OLED is a technology based on the use of organic light emitting diodes. They are used in very thin film panels (film) which, inside the displays, produce their own light.
OLEDs are particularly popular in large lighting equipment, as well as displays and screens. Even flexible screens can be produced using OLED technology, the films being foldable and rollable.
LED, OLED, LCD and their differences
The best known and most widely used are probably conventional LEDs. They were only used as control lights or in LED displays for clocks and measuring devices, as they initially had limited brightness.
Over time, however, the brightness of light-emitting diodes (in this case consisting of inorganic material) has increased significantly, so that they can be used in more and more fields, including as a light source.
LEDs are also used for the backlighting of LCD displays.
By using RGB LEDs, it is possible to produce displays with a relatively low resolution, which are especially suitable for large-scale applications. OLEDs are a modern technology with the help of which large light sources and screens can be produced. Unlike LEDs, they require a completely different manufacturing process.
Flat design thanks to thin film technology
The specialty of thin-film technology lies in the fact that, thanks to it, it is possible to produce extremely thin films, semiconductor layers only a few nanometers thick up to a few micrometers thick.
Advantages of OLEDs
Unlike LCD screens, displays made with OLEDs generate their own light, so they don’t need backlighting. This means that an important cost and energy factor is eliminated. At the same time it will still be possible to obtain very high resolution monitors and displays. Here are the main advantages of OLED:
- OLED-equipped displays produce significantly higher contrast than standard LCD displays.
- The lighting of individual pixels can be controlled separately (which is why black will be a solid black and not a particularly dark grey).
- Displays made with the help of OLEDs are extremely energy efficient.
- Viewing angle is significantly wider than comparable LCD displays.
- Displays made with OLED offer very fast response times (or image changes).
But there are also disadvantages
OLED-equipped displays and screens offer many benefits, however, they also have some drawbacks, including the following:
- Producing OLED-equipped displays is (still) quite expensive.
- They are more sensitive to many substances and therefore require very good encapsulation, which in turn can compromise the flexibility of the components.
- The light output is slightly lower than LEDs made with inorganic materials.
- OLEDs are much more sensitive to high humidity or temperature changes. When used as a light source, OLEDs have a lower luminous efficacy than LEDs.
- They can show failures very quickly if they are used excessively, areas that are no longer illuminated (so-called dark spots) may appear.
Organic LEDs based on carbonaceous substances
Of course, OLEDs are produced using chemically complex processes, which is why the term organic sounds a bit ambiguous. After all, these are electronic components dealing with substances such as silicon. Indeed, the organic light emitting diode or LED bases its name on the English term “organic,” which should be mentioned in this context together with the carbon-containing components of this semiconductor technology.
OLEDs with different luminous colors and their duration
As with conventional LEDs, the production of OLEDs with different luminous colors is based on the use of different materials. This creates a problem, as the red, green and blue light spots needed to generate all the colors of the visual spectrum are made up of different materials that have different lifetimes. In particular, in the production of screens, this means that color changes can occur on the screens over time.
Differences in electrical control of displays
Unlike LCD displays, OLED-equipped displays are self-illuminating, which means they do not require any additional backlighting. However, while OLEDs are self-luminous, they require much more electrical power to control.